V2EX C++
WebServer 异步日志模块, Log 类构析导致线程死锁, 不知如何解除异步线程阻塞
tracker647 2022-09-30 20:07:52 +08:00 1857 次点击这是一个创建于 1172 天前的主题,其中的信息可能已经有所发展或是发生改变。
测试异步日志发现程序一直卡着,调了半天才发现感觉可能是线程死锁了,gdb 查了两个线程 bt 果然是,主线程调用delete m_queue时要构析条件变量, 然而另一个线程已经用条件变量 wait 拿到互斥锁阻塞自己没法退出,导致主线程得一直等待。
把~Log 的delete m_queue一行删除就解决了,但想尝试做到既能内存 0 泄露又能正常退出程序, 问题是不知道怎么解决工作线程的 wait 状态。
一开始以为在~block_queue 部分加入m_cond.broadcast()就能解除工作线程 wait 状态了,毕竟是主程序调用的~block_queue, 然而不知道为何仍旧死锁。
热心的群友们有何良方吗?
log.h
#ifndef LOG_H #define LOG_H #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<stdarg.h> #include<time.h> #include<sys/time.h> #include<queue> #include<assert.h> #include "../lock/locker.h" #include "../log/block_queue.h" using namespace std; class Log{ public: Log(); ~Log(); void init(const char *file_path, int log_buf_size = 8192, int max_line = 80000, int queue_size = 800); static Log* get_instance(){ static Log instance; return &instance; } static void* async_write_thread(void *args){ Log::get_instance()->async_write_log(); return 0; }; void write_log(int level, const char *format,...); void flush() { m_mutex.lock(); fflush(m_fp); m_mutex.unlock(); }; private: char *get_current_time(char *time_buf, const char *format); void async_write_log(){ string logstr; while(m_is_async && m_block_queue->pop(logstr)){ m_mutex.lock(); if(DEBUG) printf("log puts\n"); fputs(logstr.c_str(),m_fp); m_mutex.unlock(); } if(DEBUG) printf("thread end\n"); }; private: char m_log_dir[128]; //日志存放目录 char m_log_name[128]; //日志名 FILE *m_fp; bool m_is_async; //异步日志模式,控制异步线程 int m_today; int m_max_line; int m_line_cnt; int m_wlog_buf_size; char *m_wlog_buf; locker m_mutex; block_queue<string> *m_block_queue; }; #define LOG_DEBUG(format, ...) {Log::get_instance()->write_log(0,format,##__VA_ARGS__); Log::get_instance()->flush();} #define LOG_INFO(format,...) {Log::get_instance()->write_log(1,format,##__VA_ARGS__); Log::get_instance()->flush();} #define LOG_WARN(format, ...) {Log::get_instance()->write_log(2,format,##__VA_ARGS__); Log::get_instance()->flush();} #define LOG_ERROR(format, ...) {Log::get_instance()->write_log(3,format,##__VA_ARGS__); Log::get_instance()->flush();} #endif //LOG_H locker.h
#ifndef LOCKER_H #define LOCKER_H #include<exception> #include<pthread.h> #include<semaphore.h> class sem{ public: sem(){ if(sem_init(&m_sem, 0, 0) != 0){ throw std::exception(); } } bool wait(){ return sem_wait(&m_sem) == 0; } bool post(){ return sem_post(&m_sem) == 0; } ~sem(){ sem_destroy(&m_sem); } private: sem_t m_sem; }; class locker{ public: locker(){ if(0 != pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, NULL)){ throw std::exception(); } } pthread_mutex_t *get(){ return &m_mutex; } bool lock(){ return pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex) == 0; } bool unlock(){ return pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex) == 0; } ~locker(){ pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex); } private: pthread_mutex_t m_mutex; }; class cond{ public: cond(){ if(0 != pthread_cond_init(&m_cond,NULL)){ throw std::exception(); } } ~cond(){ pthread_cond_destroy(&m_cond); } bool wait(pthread_mutex_t *m_mutex){ int ret = pthread_cond_wait(&m_cond,m_mutex); return ret == 0; } bool signal(){ int ret = pthread_cond_signal(&m_cond); return ret == 0; } bool broadcast(){ int ret = pthread_cond_broadcast(&m_cond); return ret == 0; } private: pthread_cond_t m_cond; }; #endif block_queue.h
#ifndef BLOCK_QUEUE #define BLOCK_QUEUE #include<queue> #include "../lock/locker.h" template <typename T> class block_queue{ public: block_queue(int sz):m_maxsize(sz){} //往阻塞队列加入日志 string bool push(const T &items){ m_mutex.lock(); //如果队列已满,需通知消费者 if(m_queue.size() >= m_maxsize){ m_cond.broadcast(); m_mutex.unlock(); return false; } m_queue.push(items); m_cond.broadcast(); m_mutex.unlock(); return true; } bool pop(T &items){ m_mutex.lock(); //若队列为空,需等待条件变量 while(m_queue.size() <= 0){ if(!m_cond.wait(m_mutex.get())){ m_mutex.unlock(); return false; } } items = m_queue.front(); m_queue.pop(); m_mutex.unlock(); return true; } bool full(){ m_mutex.lock(); if (m_queue.size() >= m_maxsize){ m_mutex.unlock(); return true; } m_mutex.unlock(); return false; } bool empty(){ m_mutex.lock(); if(m_queue.size() == 0){ m_mutex.unlock(); return true; } m_mutex.unlock(); return false; } ~block_queue(){ m_cond.broadcast(); } private: int m_maxsize; locker m_mutex; cond m_cond; std::queue<T> m_queue; }; #endif testlog.cpp
#include"log.h" #include<unistd.h> int main(){ Log::get_instance()->init("testfile"); LOG_INFO("This is a test message:)"); sleep(3); const char *mes = "log ends"; write(1,mes,strlen(mes)); printf("log ends\n"); return 0; } 现象:
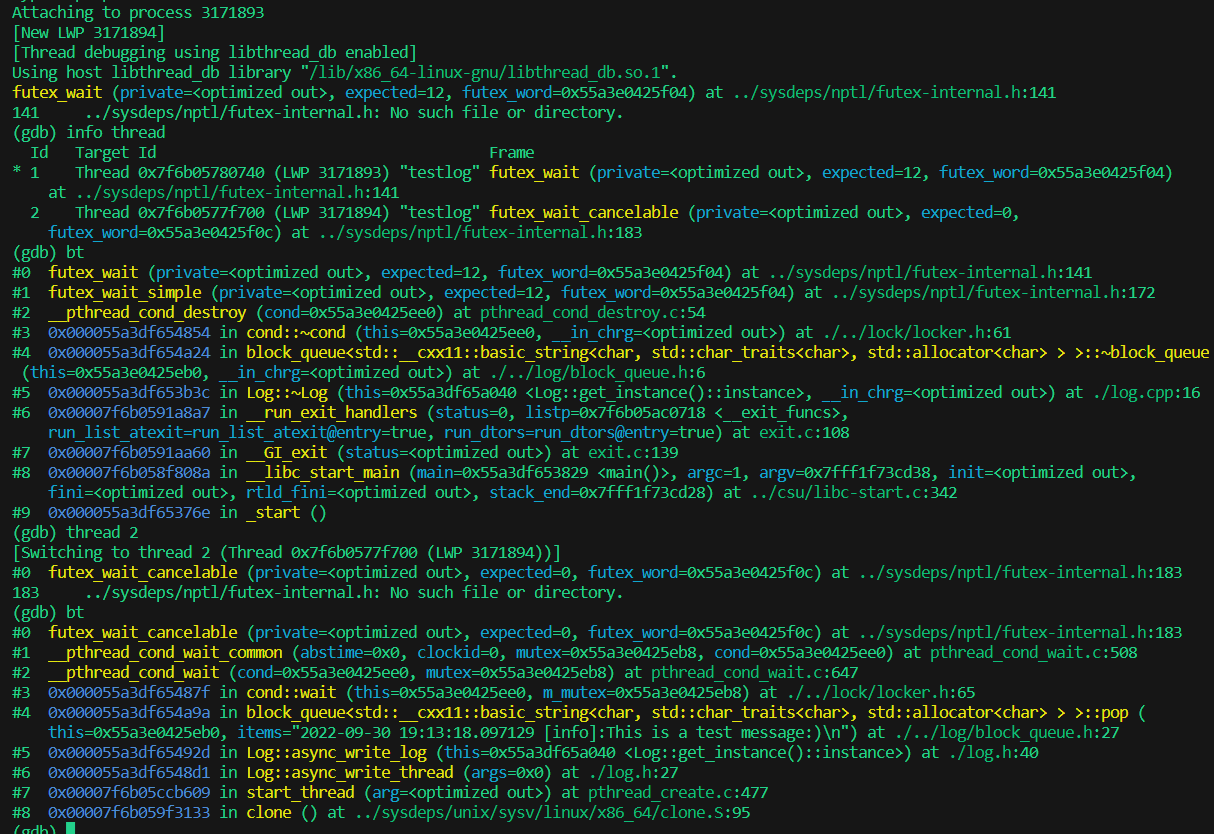
1 tracker647 OP 一番研究后找到一个解决思路, 首先日志类已经设了一个`m_is_async`的 bool 变量用于打破工作线程的循环,而 pop 条件变量的解锁条件是阻塞队列内有 push 东西经历,于是在`~Log`放了一行操作让`m_queue`push 东西打破工作线程的阻塞状态退出,工作线程再次 while 检查就会发现`m_is_async`已经被设为 false 了,从而正常退出。 ``` //Log 类 Log::Log(){ m_line_cnt = 0; m_is_async = true; memset(m_log_dir,0,sizeof(m_log_dir)); memset(m_log_name,0,sizeof(m_log_name)); } Log::~Log(){ if (m_fp != NULL){ fclose(m_fp); } m_is_async = false; delete[] m_wlog_buf; m_block_queue->push("log end"); //用于结束日志线程的阻塞状态,不加会死锁 delete m_block_queue; } void async_write_log(){ string logstr; while(m_is_async && m_block_queue->pop(logstr)){ m_mutex.lock(); fputs(logstr.c_str(),m_fp); m_mutex.unlock(); } }; ``` |
2 luassuns 2022-10-11 21:57:01 +08:00 @tracker647 应该先 `m_is_async = false;` 再 fclose ,而且应该在置 false 后 join thread 等待线程结束,要不可能会 fputs 到 close 的 handle 里。 |
